Abstract
INTRODUCTION: Despite the current excellent prognosis of chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) patients, a significant percentage of patients will not achieve a deep molecular response that would allow them to discontinue treatment. Immune cell-mediated approaches such as allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation and interferon were the mainstays for the treatment of CML before tyrosine kinases inhibitors arrival. The programmed death-1 (PD-1)/programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) axis has been shown as a potential target in CML in murine model of CML. A previous study showed an adequate safety profile of dasatinib in combination with nivolumab in CML pts failing to previous TKIs.
AIMS: To evaluate the safety and efficacy of bosutinib in combination with atezolizumab for CML newly diagnosed patients.
PATIENTS AND METHODS: Phase Ib/II, single arm, open-label and dose-escalation study designed to determine the safety profile and the recommended phase III dose (RP3D) of bosutinib when administered in combination with atezolizumab in naïve patients with chronic myeloid leukemia in chronic phase (Phase Ib/II). The primary endpoint was to determine the safety and tolerability of the combination therapy. Secondary endpoints were the number and rate of patients that achieve major molecular response MMR. Treatment schedule was designed in 3 phases. First therapy: 400 mg of bosutinib/day for one treatment cycle (28 days). Second therapy: 400 mg of bosutinib/day combined with either 840 mg/2 weeks or 1680 mg/4 weeks of atezolizumab for 12 cycles. Third therapy: 400 mg of bosutinib/day for 12 cycles. The incidence, nature, and severity of adverse events (AEs), serious AEs (SAEs), and AEs of special interest (AESIs) were graded according to the National Cancer Institute Common Terminology Criteria for AE (version 4). If dose-limiting toxicities (DLTs) appeared in 2 or more patients the study was terminated.
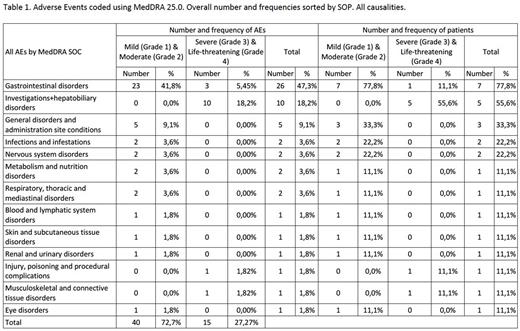
RESULTS: A total of 36 patients were initially planned to be enrolled. Due to premature study discontinuation, only 9 patients were finally recruited. 8 of them reached the 2nd therapy phase of the study and received, at least one dose of atezolizumab in combination with bosutinib. 3 patients receive one dose of 840 mg of atezolizumab, 3 patients receive 2 doses of 840 mg of atezolizumab, and 2 patients receive 3 doses of 840 mg of atezolizumab. The onset of several events affecting the liver normal function (elevation of transaminases), considered AESIs, led to the premature termination of the study after the onset 2 DLTs. Totally, 4 (50% of the patients that received treatment combination) patients withdrew due to liver toxicity (grade 3-4) (table 1). No patients suffered from liver comorbidities nor autoimmune disorders previous to study entry. One patient suffered from liver toxicity in the bosutinib monotherapy phase. All patients completely recovered after treatment interruption. Altogether, 55 AEs were reported during the study (table 1), 35 (63.6% of the total) were mild or grade 1, 5 (9.1%) moderate or grade 2, 12 (21.8%) were severe or grade 3 and 3 (5.5%) were considered life-threatening, grade 4 events, Alanine aminotransferase increased, Cholestasis and Blood bilirubin increased. The AEs were mainly gastrointestinal disorders (N=26), specially, diarrhoea (N=11), vomiting (N=6) and nausea (N=4). Of those, possibly related AEs, 19 were mild, 4 moderate, 10 severe and 3 life threatening, all 3 detected in the same patient. Regarding efficacy, at cycle 4 (3 months follow up), 100% of the patients tested (n=3) reached complete cytogenetic response.
CONCLUSIONS: We found dose limiting toxicity when combining bosutinib with atezolizumab due to serious liver toxicities events. The use of immune check points inhibitors could increase adverse events related to TKIs. This information should be taken into consideration when designing clinical trials combining these two treatments options. This study is sponsored by Pfizer.
Disclosures
García Gutiérrez:Roche: Research Funding; BMS: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Incyte: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Pfizer: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Novartis: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau. Casado Montero:Janssen: Consultancy, Research Funding; Roche: Consultancy, Research Funding; Novartis: Consultancy, Research Funding; BMS: Consultancy, Research Funding; Amgen: Consultancy, Research Funding; Takeda: Consultancy, Research Funding; Pfizer: Consultancy, Research Funding; Incyte: Consultancy, Research Funding; Abbvie: Consultancy, Research Funding; GSK: Consultancy, Research Funding; Sanofi: Consultancy, Research Funding; Beigene: Consultancy, Research Funding; Loxo: Research Funding. Gómez-Casares:Novartis: Speakers Bureau; Pfizer: Speakers Bureau; BMS: Speakers Bureau. Ferrer Marin:Incyte: Research Funding.
OffLabel Disclosure:
Bosutinib in combination with atezolizumab
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal